Blog
How IoT Works & 8 Protocols you need to know
IoT protocols are a crucial part of the IoT technology stack — without them, the hardware would be rendered useless as the IoT protocols enable it to exchange data in a structured and meaningful way. Out of these transferred pieces of data, useful information can be extracted for the end-user and thanks to it, the whole deployment becomes economically profitable
What is IoT?
IoT or Internet of Things is a huge ecosystem of interconnected networks which is expanding daily from the last two decades. They are edge devices and sensors, which can be used in office, buildings, vehicles, security systems, actuators, etc.

Internet of Things can also be referred to as the Internet of Everything (IoE) as all the devices are connected with each other or to the internet. Every device in the network, will collect the data, process it and then transmit.
Scope of IoT
With billions of such devices being connected to the internet, the scope of IoT is beyond imagination.
Many people have dreamt of a house like Stark Tower, where you walk in as Ironman, and Jarvis handles all your daily jobs with the help of your command. While Ironman’s suit might be a distant reality, Jarvis is already here. (Only Marvel Fans would relate to this excerpt)
With the help of the internet and all the connected devices, Jarvis is not far as various automation systems are already available in the market.
How automation can be done?
Is the world ready for the automation yet?
Ready or not, automation has started ruling the market. IoT devices are available almost in everyday life like home, office, medical, education, security, etc. Their demand is increasing day by day. For example,
What would you do if you want to buy something?
You will ask your digital assistant (Google, Alexa, Cortana, etc) to search it for you. After this, Google will show you some results. You will be wondering how the searches are related to your previous searches. It is because your device learns the pattern behind your expenditure. Every IoT device keeps on learning new things every day.
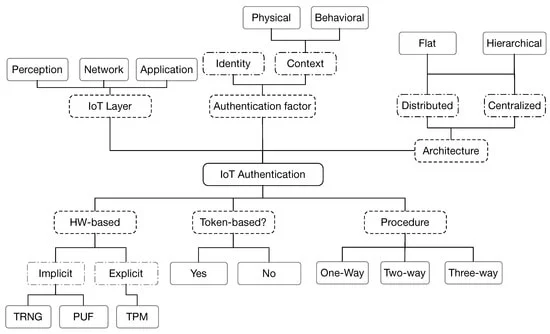
The Internet of Things (IoT) is the ability to provide everyday devices with a way of identification and another way for communication with each other. The spectrum of IoT application domains is very large including smart homes, smart cities, wearables, e-health, etc. Consequently, tens and even hundreds of billions of devices will be connected. Such devices will have smart capabilities to collect, analyze and even make decisions without any human interaction.
Security is a supreme requirement in such circumstances, and in particular, authentication is of high interest given the damage that could happen from a malicious unauthenticated device in an IoT system. This paper gives a near-complete and up-to-date view of the IoT authentication field. It provides a summary of a large range of authentication protocols proposed in the literature. Using a multi-criteria classification previously introduced in our work, it compares and evaluates the proposed authentication protocols, showing their strengths and weaknesses, which constitutes a fundamental first step for researchers and developers addressing this domain.
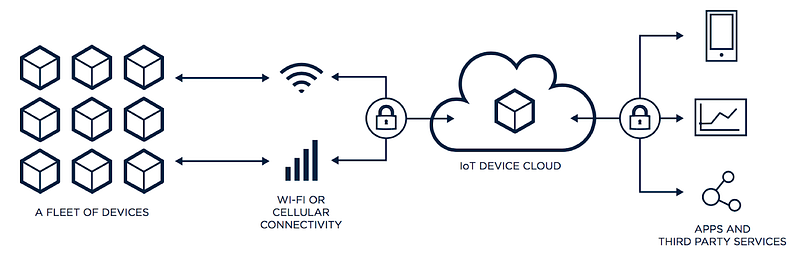
How IoT work?
IoT is a next-generation technology system consisting of devices and sensors. The devices and sensors connect to the cloud and communicate through some kind of connectivity. The data enters the cloud, the data is being assessed and processed and later, the same data takes action.
Here is an image depicting the working of IoT
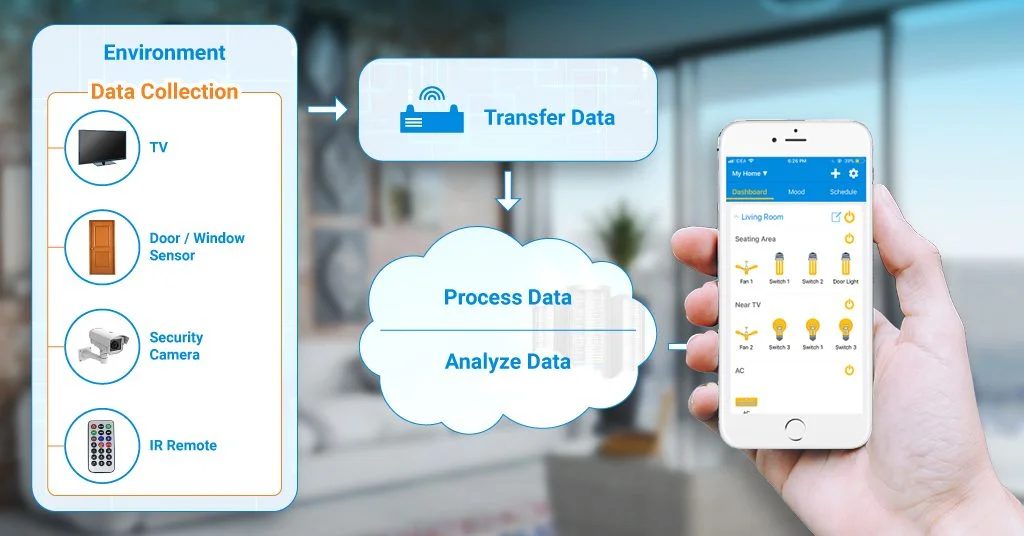
1. Data Collection
Sensors or gadgets help in gathering exact information from the environment. The majority of this gathered information can have different degrees of complexities running from a basic temperature checking the sensor to a home automation system.
Every device keeps collecting data based on their surroundings with the help of sensors embedded in them. After the collection, the data is transferred through the gateway for analyzing.
A gadget can have numerous sensors that can package together to accomplish something other than sense things. For instance, our telephone is a gadget that has different sensors, for example, GPS, accelerometer, camera, however, our telephone does not just detect things.
The most important step is to pick and gather information from the environment.
2. Transfer data
After the collection of data is done, the data is transferred to the cloud for further analyzing or the device itself analyzes the data. To transfer the data, one needs a gateway for connecting to the cloud. The data can be transferred to the cloud through various channels like Wifi, Bluetooth, cellular networks, satellite networks, etc. The transferred data is then analyzed for further processing.
3. Analyze Data
The collected data is then analyzed in the cloud and operations are performed on it. This data is processed further for user interaction.
4. Process Data
When the information is gathered and it gets to the cloud, the software starts processing the obtained information.
This can range from something extremely simple like watching the temperature on devices such as AC or warmers is inside a satisfactory range. And very difficult, for example, recognizing objects, (for example, interlopers in your home) utilizing PC vision on record. There might be chances where we need some user interaction also.
The data processing is done in the cloud as soon as the data reaches the cloud. Even the smallest data like the temperature of the room and complex data like the movement of celestial objects are processed in the cloud.
Most of the devices are now fully automated which can be handled without the intervention of any user. But, still, there are some devices that need human intervention to operate with ease.
For example, if you are using a smart refrigerator then you have to set the temperature for the first time and then it will adjust itself automatically.
Another example is of air conditioner, where it will adjust the temperature according to the conditions. But, if there are 5 persons in the room then each will have different preferences. So, some intervention is required. Here, the user interface comes into the picture.
5. User Interface
The user interface helps the user to control whatever is happening in the devices. The interface is a platform to connect with the devices. You should have a hang of what is happening in your IoT devices. Otherwise, the automation can backfire also.
For example, when you forget to turn off your AC, then it would still be a waste of electricity even if it keeps on adjusting its temperature.
A client at times may have an interface through which they can effectively monitor their IoT framework. For instance, a client has a camera introduced at his home, he can check all the video recordings through a web server.
Protocols of IoT
To communicate with the cloud or within the network, the devices require some medium.
IoT protocols provide devices with a medium to communicate securely with each other and with the cloud. These protocols vary depending on the range, power, and the requirement. IoT devices are connected to the internet via IP(Internet Protocol). For data transfer, HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) is used.
For transfer of data locally, Bluetooth and RFID protocols are used whereas, long-distance WiFi protocol is used.
1. Bluetooth
Who doesn’t know about this protocol? From the time it came into existence, Bluetooth has disrupted the entire market.
Bluetooth is one of the most widely used wireless protocols for short-range communication. This IoT protocol is perfect for short-range, low power, low cost and secure communication between the devices.
Bluetooth provides ease of control and is preferable for small data transfers between the devices.
Bluetooth is a 2.4GHz short-range private area network. It is used in everyday devices like Speakers, headphones, and smartphones.
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) (4.0) is a low energy version of Bluetooth which is ideal for IoT devices. It requires low power for operating as compared to Bluetooth. By consuming less power, it will allow us to save cost.
Due to these features, BLE is also marketed as Bluetooth Smart. This version of Bluetooth enables us to connect to smart-watches and other smart devices. It is ideal for transferring small data in a local network.
Bluetooth 5.0 is the latest Bluetooth version available in the market.

2. Zigbee
Zigbee is a 2.4GHz mesh personal area network. Zigbee is a low data rate technology which is a requirement in IoT devices these days. It provides a low cost and low energy solution as compared to other high rate devices.
Zigbee is used in the devices which support low data transfer. It is used in controlling mesh networks like smart street lights, electric meters, wireless thermostats which require low power consumption. Its major application is in home automation technology.
Zigbee is more like a B2B service than a B2C service. It is more useful to industrialists than to customers. A real-life application of Zigbee is Spikebot.
3. WiFi
Wireless Fidelity or WiFi is the most widespread network protocol. It is a local area network used for connecting a broad network of computers. It has longer range as compared to Bluetooth, Zigbee, and other protocols.
WiFi is having a high rate data transfer along with the capacity of handling large data. Its range is approx. 50m and it operates on two frequencies: 2.4GHz and 5GHz. Its cost depends upon the type of frequency and speed you choose to operate upon.
WiFi is present everywhere from mobile phones to AC, lights to the washing machine.
4. LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network)
As its name suggests, LoRaWAN is a low power, long-ranged WAN. LoRaWAN is used to detect low power signals from long distances. It was designed to connect millions of smart devices having low power and batteries. This protocol is mainly used in smart cities.
The frequency of LoRaWAN differs for every network. The data rates also differ from a range of 0.3 to 50 kbps. And the range also differs from a few km to around 20kms.
The practical application of LoRaWAN is traffic monitoring and controlling of street lights in the city. LoRaWAN protocol can be used to control the intensity and time of Street lights.
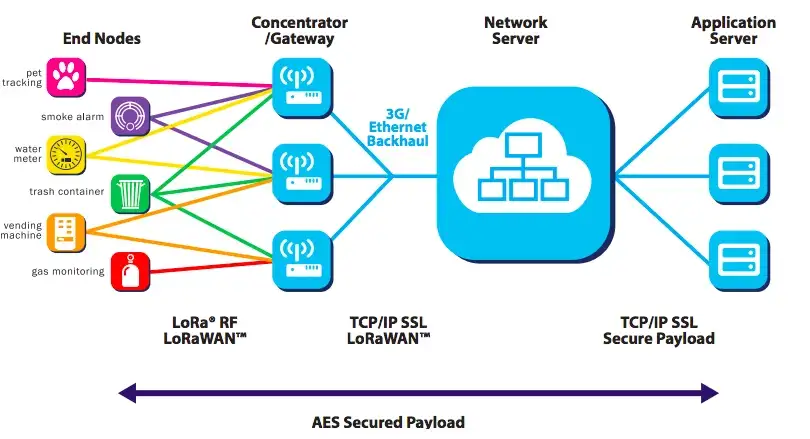
5. MQTT(Message Queue Telemetry Transport)
MQTT is a machine to machine(M2M) communication protocol. The basic task of MQTT is to collect data from various electronic devices present around and remote monitoring.
MQTT was designed as a lightweight publish/subscribe protocol where a simple code is used to operate multiple small devices.
MQTT protocol has three main components. They are:
Subscriber
Publisher
Broker
The task of the publisher is to collect data and transmit it to the subscriber with the help of a broker.
The broker is responsible for security. The broker checks the authorization of both, subscribers and publishers by performing the handshaking process.
MQTT runs on the TCP protocol for supplying a simple and reliable source of data.
MQTT is used for IoT devices which has low memory consumption like fire sensors, car sensors, etc.
6. AMQP( Advanced Message Queuing Protocol )
AMQP is a TCP layer, open-source protocol. It is message-oriented and is designed for a middleware environment that provides routing and queuing. Also, it is responsible for making a point to point connection while sending messages securely between industries. However, it is portable, efficient and secure.
AMQP protocol is fast and it guarantees delivery with acknowledgement of received messages. It works well in multi-client environments and provides a means for authorizing tasks and making servers handle more requests.
AMQP has three components for exchanging the messages. They are:
Exchange
Message Queue
Binding
In the Exchange part, the message is received from primary sources and is routed to the Message Queues.
The Message Queue stores the message until the message is processed by the client app thoroughly.
The binding component states the relationship between the Exchange component and Message Queue component. All these components help us in creating a relation between two messages.
The practical application of AMQP is Loan providing company, where the reminder for premium must reach the user. Whenever the server sends the message, AMQP ensures that the message reaches the user.
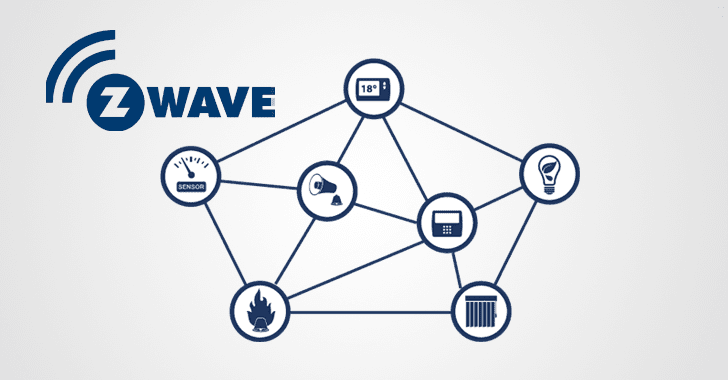
7. Z-Wave
Z-Wave is a wireless communication protocol. It was found as a cost-effective alternative to Zigbee. Z-Wave protocol uses low range radio waves for communication. It is mainly used in the Home Automation system.
It offers low power connectivity than WiFi and longer range than Bluetooth.
Z-Wave is a mesh network with two-way communication. Having a mesh network is very beneficial. Each device that gets added into the network strengthens it by acting as repeaters.
Every device on a WiFi network needs to be connected with the router. Whereas, in Z-Wave every device is connected to the central hub with Z-Wave protocol and the hub is connected to the internet. Every device present in the network are interlinked with each other and not to the internet.
Z-Wave operates on the 800-900MHz radio frequency range, unlike Zigbee which operates on 2.4 GHz. The lower frequency serves as an advantage to Z-Wave as it doesn’t have to face interference as that of Zigbee.
Every Home Automation system is nowadays using the Z-Wave protocol to control multiple devices without any hassle.
8. RFID
RFID or Radio Frequency Identification is a method of automatic identification and data capture (AIDC). It works on wireless technology and uses electromagnetic fields to identify objects.
An RFID system is made up of two things: RFID tag and RFID reader. To read the tag on the object doesn’t need to be in the line of sight. Every RFID tag has a unique serial number.
There are two types of tags used in RFID. Passive and Battery powered(Active). The passive tag draws power from the reader and the active tag has its transmitter and a small source (battery) connected to it. The range of the tags depends upon the type of tags.
The main application of RFID technology is to check stock or prices in an inventory.
IoT is a huge topic that cannot be explained in a day. But, we have tried our bit to explain it in an easy way. Stay tuned for further information as we explore the field of IoT.
Takeaway
If you wish to transform your world with digitally enabled smart products and services, we suggest you with IoT and IIoT. Visit our website for more information.